Conversations with Messages
Overview
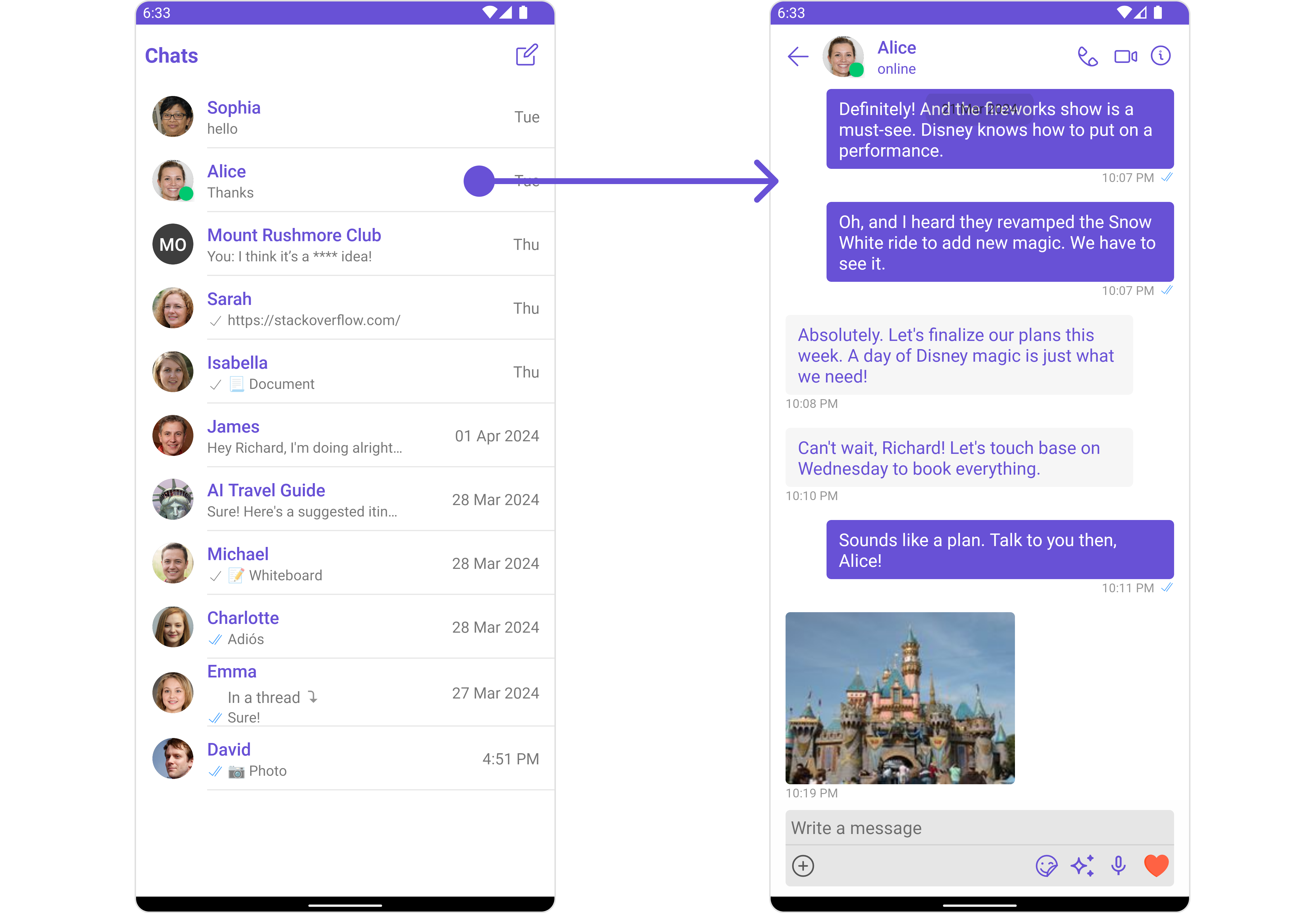
The ConversationsWithMessages is a Composite Component encompassing components such as Conversations, Messages, and Contacts. Each of these component contributes to the functionality and structure of the overall ConversationsWithMessages component.
| Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Conversations | The Conversations component is designed to display a list of either User or Group. This essentially represents your recent conversation history. |
| Messages | The Messages component is designed to manage the messaging interaction for either individual User or Group conversations. |
| Contacts | The CometChatContacts component is specifically designed to facilitate the display and management of both User and Groups. |
Usage
Integration
There are multiple ways in which you can use ConversationsWithMessages in your app.
Layout File: To use ConversationsWithMessages in your `layout_activity.xml, use the following code snippet.
<com.cometchat.chatuikit.conversationswithmessages.CometChatConversationsWithMessages
android:id="@+id/conversation"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
Activity: To use ConversationsWithMessages in your `Activity, use the following code snippet.
- Java
- Kotlin
@Override
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View? {
return cometChatConversationsWithMessages(context)
}
override fun onCreateView(inflater: LayoutInflater,container: ViewGroup?,savedInstanceState: Bundle?): View {
return cometChatConversationsWithMessages(requireContext())
}
Fragment: To use ConversationsWithMessages in your `Fragment, use the following code snippet.
- Java
- Kotlin
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(new cometChatConversationsWithMessages(this));
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(cometChatConversationsWithMessages(this))
}
Actions
Actions dictate how a component functions. They are divided into two types: Predefined and User-defined. You can override either type, allowing you to tailor the behavior of the component to fit your specific needs.
While the ConversationsWithMessages component does not have its actions, its components - Conversation, Messages, and Contacts - each have their own set of actions.
The Action of the components can be overridden through the use of the Configurations object of its components. Here is an example code snippet.
- Java
- Kotlin
ConversationsConfiguration configuration = new ConversationsConfiguration();
configuration.setOnError((context, e) -> {
//Your Error handling action.
});
ContactsConfiguration contactsConfiguration = new ContactsConfiguration();
contactsConfiguration.setOnSubmitIconClick((context, list, list1) -> {
//Your action on submit click.
});
val configuration = ConversationsConfiguration()
configuration.onError = { context, e ->
// Your error handling action
}
val contactsConfiguration = ContactsConfiguration()
contactsConfiguration.onSubmitIconClick = { context, list, list1 ->
// Your action on submit click
}
The ConversationsWithMessages component overrides several actions from its components to reach its default behavior. The list of actions overridden by ConversationsWithMessages includes:
- ItemClickListener : By overriding the
ItemClickListenerof the Conversation Component, ConversationsWithMessages achieves navigation from Conversation to Messages component.
Filters
Filters allow you to customize the data displayed in a list within a Component. You can filter the list based on your specific criteria, allowing for a more customized. Filters can be applied using RequestBuilders of ChatSDK.
While the ConversationsWithMessages component does not have filters, its components do, For more detail on individual filters of its component refer to Conversations Filters and Messages Filters.
By utilizing the Configurations object of its components, you can apply filters.
In the following example, we're filtering Conversation to only show User
- Java
- Kotlin
ConversationsConfiguration configuration = new ConversationsConfiguration();
ConversationsRequest.ConversationsRequestBuilder builder = new ConversationsRequest.ConversationsRequestBuilder();
builder.setConversationType(CometChatConstants.CONVERSATION_TYPE_USER);
builder.setLimit(50);
configuration.setConversationsRequestBuilder(builder);
val configuration = ConversationsConfiguration()
val builder = ConversationsRequest.ConversationsRequestBuilder()
builder.setConversationType(CometChatConstants.CONVERSATION_TYPE_USER)
builder.setLimit(50)
configuration.conversationsRequestBuilder = builder
Events
Events are emitted by a Component. By using event you can extend existing functionality. Being global events, they can be applied in Multiple Locations and are capable of being Added or Removed.
The ConversationsWithMessages does not generate its events but its component does. For a full list of these events, you can refer to Conversations events and Messages events.
In the following example, we're incorporating observers for the ConversationDeleted event of Conversations and the MessageSent event of the Messages component.
- Java
- Kotlin
CometChatConversationEvents.addListener("LISTENER_TAG", new CometChatConversationEvents() {
@Override
public void ccConversationDeleted(Conversation conversation) {
// Your Action
}
});
CometChatMessageEvents.addListener("LISTENER_TAG", new CometChatMessageEvents() {
@Override
public void ccMessageSent(BaseMessage baseMessage, int status) {
// Your Action
}
});
CometChatConversationEvents.addListener("LISTENER_TAG", object : CometChatConversationEvents() {
override fun ccConversationDeleted(conversation: Conversation) {
// Your Action
}
})
CometChatMessageEvents.addListener("LISTENER_TAG", object : CometChatMessageEvents() {
override fun ccMessageSent(baseMessage: BaseMessage, status: Int) {
// Your Action
}
})
Customization
To fit your app's design requirements, you have the ability to customize the appearance of the ConversationsWithMessages component. We provide exposed methods that allow you to modify the experience and behavior according to your specific needs.
Style
Using Style you can customize the look and feel of the component in your app, These parameters typically control elements such as the color, size, shape, and fonts used within the component. ConversationsWithMessages component doesn't have its own style parameters. But you can customize its component styles. For more details on individual component styles, you can refer Conversation Styles, Messages Styles, and Contacts Styles
Styles can be applied to SubComponents using their respective configurations.
Example
- Java
- Kotlin
CometChatConversationsWithMessages conversationsWithMessages = findViewById(R.id.conversation);
ConversationsStyle conversationsStyle = new ConversationsStyle();
conversationsStyle.setBackground(Color.parseColor("#757575"));
conversationsStyle.setSeparatorColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"));
conversationsStyle.setTitleColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"));
ConversationsConfiguration configuration = new ConversationsConfiguration();
configuration.setConversationsRequestBuilder(builder);
configuration.setStyle(conversationsStyle);
conversationsWithMessages.setConversationsConfiguration(configuration);
val conversationsWithMessages: CometChatConversationsWithMessages = findViewById(R.id.conversation)
val conversationsStyle = ConversationsStyle()
conversationsStyle.setBackground(Color.parseColor("#757575"))
conversationsStyle.setSeparatorColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"))
conversationsStyle.setTitleColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"))
val configuration = ConversationsConfiguration()
configuration.setConversationsRequestBuilder(builder)
configuration.setStyle(conversationsStyle)
conversationsWithMessages.setConversationsConfiguration(configuration)
Functionality
These are a set of small functional customizations that allow you to fine-tune the overall experience of the component. With these, you can change text, set custom icons, and toggle the visibility of UI elements.
Set User
You can utilize the .setUser(user) function with a User object as input to ConversationsWithMessages. This will automatically guide you to the Messages component for the designated User.
- Java
- kotlin
conversationsWithMessages.setUser(user);
conversationsWithMessages.user = user
Set Group
You can utilize the .setGroup(group) function with a Group object as input to ConversationsWithMessages. This will automatically guide you to the Messages component for the designated Group.
- Java
- kotlin
conversationsWithMessages.setGroup(group);
conversationsWithMessages.group = group
Components
Nearly all functionality customizations available for a Component are also available for the composite component. Using Configuration, you can modify the properties of its components to suit your needs.
You can find the list of all Functionality customization of individual components in Conversations , Messages, and Contacts
Example
ConversationsConfiguration conversationsConfiguration = new ConversationsConfiguration();
conversationsConfiguration.setTitle("Your Custom Title");
conversationsConfiguration.showBackButton(true);
MessagesConfiguration messagesConfiguration = new MessagesConfiguration();
messagesConfiguration.setDisableTyping(false);
messagesConfiguration.setHideMessageHeader(true);
conversationsWithMessages.setConversationsConfiguration(conversationsConfiguration);
conversationsWithMessages.setMessagesConfiguration(messagesConfiguration);
Advanced
For advanced-level customization, you can set custom views to the component. This lets you tailor each aspect of the component to fit your exact needs and application aesthetics. You can create and define your own views, layouts, and UI elements and then incorporate those into the component.
By utilizing the Configuration object of each component, you can apply advanced-level customizations to the ConversationsWithMessages.
Example
ConversationsConfiguration conversationsConfiguration = new ConversationsConfiguration();
conversationsConfiguration.setErrorStateView(R.layout.your_custom_view);
conversationsWithMessages.setConversationsConfiguration(conversationsConfiguration);
To find all the details on individual Component advance customization you can refer, Conversations Advance,Messages Advance and Contacts Advance
ConversationsWithMessages uses advanced-level customization of both Conversation & Messages components to achieve its default behavior.
-
ConversationsWithMessages utilizes the SetMenu function of the
Conversationssubcomponent to navigate the user from Conversations to Contacts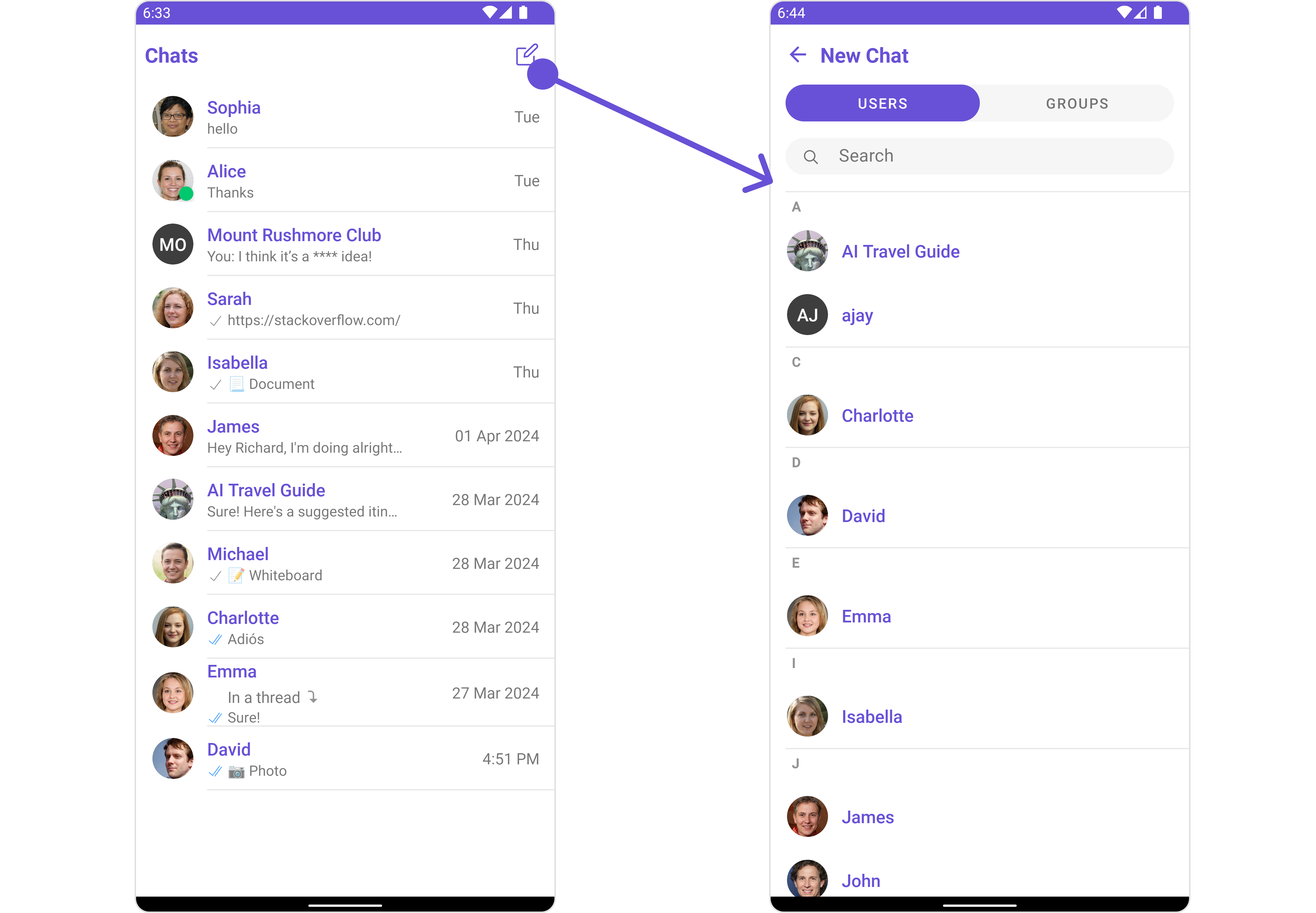
-
ConversationsWithMessages utilizes the SetMenu function of the
Messagessubcomponent to navigate the user from Messages to Details.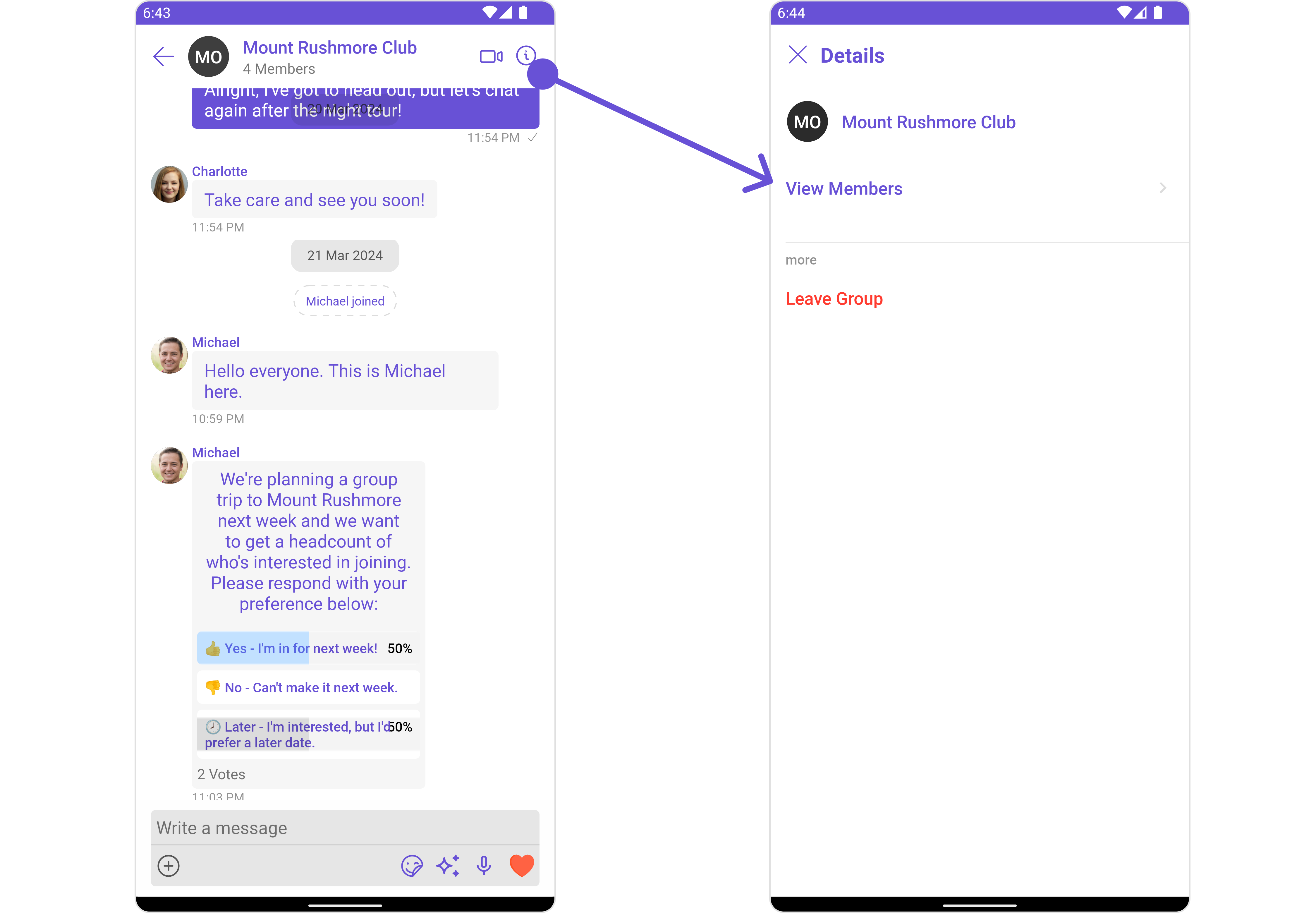
When you override .setMenu(), the default behavior of ConversationsWithMessages will also be overridden.
Configurations
Configurations offer the ability to customize the properties of each component within a Composite Component.
ConversationsWithMessages has Conversations, Messages, and Contacts component. Hence, each of these components will have its individual `Configuration``.
Configurationsexpose properties that are available in its individual components.
Conversations
You can customize the properties of the Conversations component by making use of the ConversationsConfiguration. You can accomplish this by employing the .setConversationsConfiguration() method as demonstrated below:
- Java
- Kotlin
ConversationsConfiguration configuration = new ConversationsConfiguration();
conversationsWithMessages.setConversationsConfiguration(configuration);
val configuration = ConversationsConfiguration()
conversationsWithMessages.setConversationsConfiguration(configuration)
All exposed properties of ConversationsConfiguration can be found under Conversations. Properties marked with the symbol are not accessible within the Configuration Object.
Example
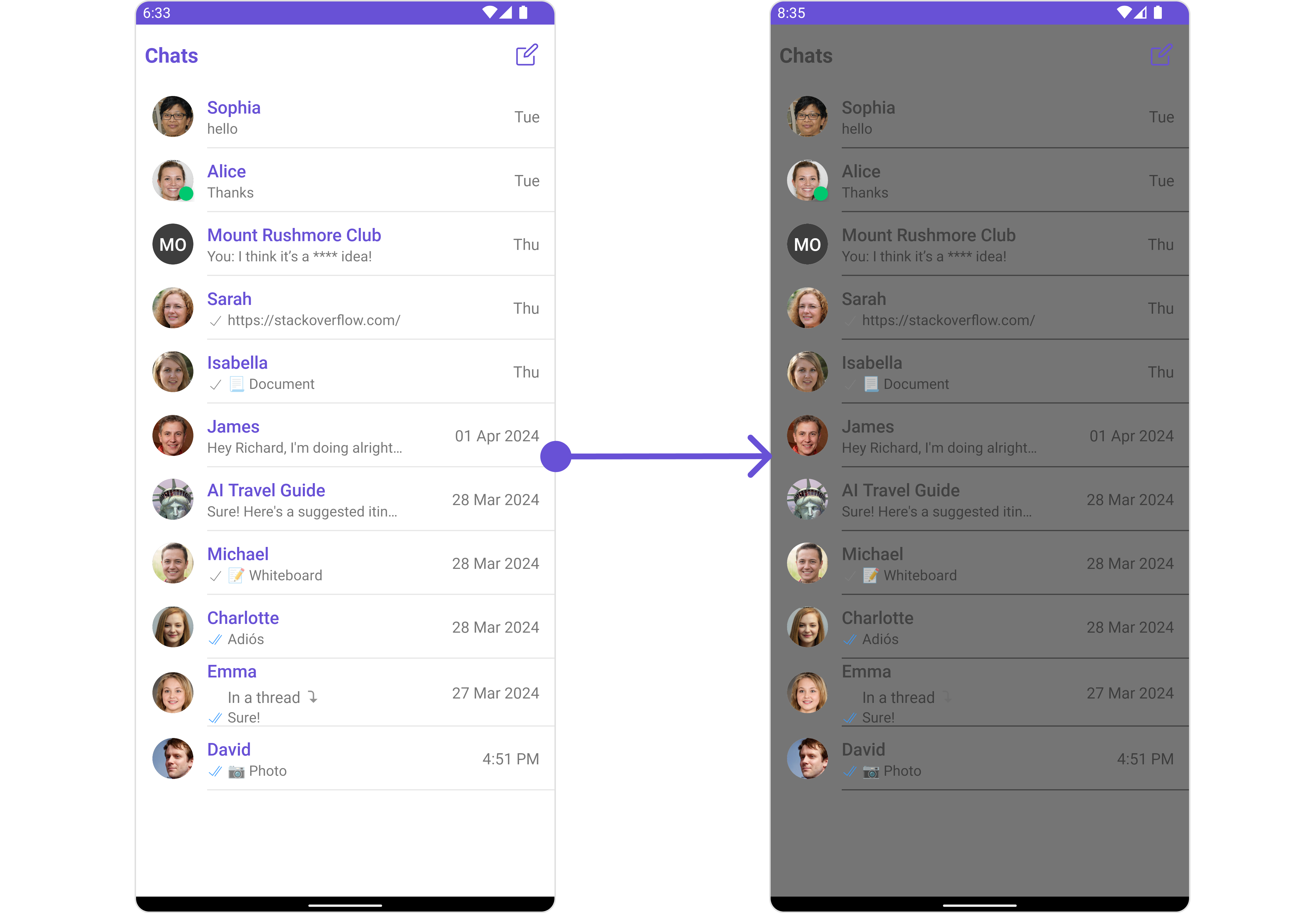
Let's say you want to change the style of the Conversations subcomponent and, in addition, you only want to display users in the conversation list.
You can modify the style using the .setStyle() method and filter the list with the .setConversationsRequestBuilder() method.
- Java
- Kotlin
CometChatConversationsWithMessages conversationsWithMessages = findViewById(R.id.conversation);
ConversationsRequest.ConversationsRequestBuilder builder = new ConversationsRequest.ConversationsRequestBuilder();
builder.setConversationType(CometChatConstants.CONVERSATION_TYPE_USER);
ConversationsStyle conversationsStyle = new ConversationsStyle();
conversationsStyle.setBackground(Color.parseColor("#757575"));
conversationsStyle.setSeparatorColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"));
conversationsStyle.setTitleColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"));
ListItemStyle listItemStyle = new ListItemStyle();
listItemStyle.setTitleColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"));
ConversationsConfiguration configuration = new ConversationsConfiguration();
configuration.setConversationsRequestBuilder(builder);
configuration.setStyle(conversationsStyle);
configuration.setListItemStyle(listItemStyle);
conversationsWithMessages.setConversationsConfiguration(configuration);
val conversationsWithMessages = findViewById<CometChatConversationsWithMessages>(R.id.conversation)
val builder = ConversationsRequest.ConversationsRequestBuilder()
builder.setConversationType(CometChatConstants.CONVERSATION_TYPE_USER)
val conversationsStyle = ConversationsStyle()
conversationsStyle.setBackground(Color.parseColor("#757575"))
conversationsStyle.setSeparatorColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"))
conversationsStyle.setTitleColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"))
val listItemStyle = ListItemStyle()
listItemStyle.setTitleColor(Color.parseColor("#424242"))
val configuration = ConversationsConfiguration()
configuration.setConversationsRequestBuilder(builder)
configuration.setStyle(conversationsStyle)
configuration.setListItemStyle(listItemStyle)
conversationsWithMessages.setConversationsConfiguration(configuration)